Chapter 2 Windows
MICROSOFT WINDOWS
Microsoft Windows operating system was developed by
Microsoft to overcome the limitations of its own MS-DOS operating
system. First successful version of this operating
system was Windows 3.0, released in 1990. Subsequently released versions were
Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows XP Professional, and
Windows Vista. The numbers associated with some of these released versions
indicate their year of release. Main features of Microsoft Windows are as
follows :
1. 1. Its native interface is a GUI. Hence, for a new user it is easier to
learn and use a
computer system.
2. Microsoft Windows was designed to be not
just an operating system but also a complete operating environment. That is,
all its programs conform
to a standard way
of working. For example, a
Microsoft Windows word processor works similarly the way a Microsoft Windows spreadsheet (or any other
type of Windows program) works. This means that experience gained by learning one Windows program is useful while using any other Microsoft Windows program.
3. It is a single-user, multitasking
operating system. That is, a user may run more than one program at a time. For example, while editing a file in foreground,
a sorting job can be run in
background. Monitor's screen can be partitioned into multiple windows and
progress of different programs can be viewed on different windows.
Parts of Windows Desktop
Following are the
main parts of windows desktop.
1.
Icons:
An icon is a small graphic lying on the desktop which is
actually an application or utility at rest. You can simply double click the
icon to run the associated application. The icons
can be further classified into application icons, shortcuts and document icons.
There is no limit to the number and type of icons you can place on your windows desktop.
2.
Wallpaper:
A large graphic file that spreads over entire screen of your monitor
is called wallpaper. Windows enables you to
change your desktop wallpaper according to your choice. Many readymade wallpapers are inbuilt to windows.
You can also download images
from the Internet and set them as wallpaper. You can also transfer
images from digital camera and set them as wallpaper. You can even create your
own paintings in Paintbrush and set them as
wallpaper.
3.
Taskbar:
Taskbar is a horizontal bar situated at the bottom
of Windows desktop. It enables you to manage multiple applications which
are running simultaneously. As Windows is a multitasking
operating system, multiple
applications may be running at one time. Just click on the application
name on the taskbar to activate the application.
4.
Start
Button: Start button is a small button present on the left of
taskbar. You can click it to display a
popup menu that contains many options
like programs, documents, settings, help, run, find and shutdown. Each of these options has a
specific functionality. Following are the components
of start menu
COMPONENTS OF A WINDOW
An application
window is the rectangular area that contains
an application. For example, when you open
paintbrush from Start □Programs
□Accessories □Paint, it is opened in an application window. The application
window that is currently receiving
the user input is called Active Window.
Multiple application windows may be opened at a time but only one widow can be
the active window. This means, you
can supply input to only one window at one time. The application window
can contain multiple instances of application at one time. Just click on the
window to make it active.
Parts of Application Window
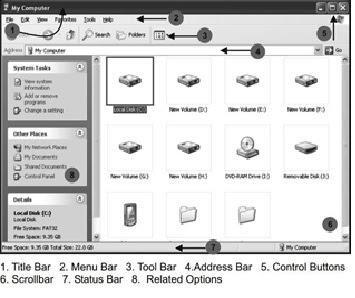
Each application window has a Title Bar, Menu Bar, Tool
Bar, Minimize button, Restore button and Maximize button. The figure 1 displays
an example of My Computer window.
The application window has the following main parts:
1. Title
Bar: It is a horizontal bar on the top of the window. It displays the title of the
window. In figure 1, the dark strip containing the title My
Computer is title bar. Title Bar
also contains window buttons and it also shows control menu when you
click its icon on the title bar.
2. Menu Bar: The
menu bar contains different menus with
different options to perform different commands. A
drop down list of options is
displayed when you click on a
menu item. Each of these options represents a
command.
 |
| Parts of Window |
3. Toolbar: Toolbar is a horizontal bar with various command buttons. These buttons provide a shortcut to access to commonly used menu commands. A click on the particular button is required to trigger the command associated with it. For example, clicking on the Open icon will bring Open dialog box.
4. Address Bar: It is a horizontal bar under the toolbar that displays the path or name of the current folder. It is present in some special type of applications. In figure 1(b), My Computer has been displayed in the address bar. If you are working in a folder Windows under C drive, the address bar will show C:\Windows.
5. Minimise Button: It is the first out of the three buttons displayed on the right end of title bar. A click on this button will deactivate the current window and place it on taskbar. The minimised application will display its name. The figure 2 displays a taskbar having notepad application in minimised form.
6. Restore (Maximized) Button: It is the second button out of three buttons displayed on the right end of title bar. On clicking this button the size of current window is restored (reduced) from maximized state and maximized from reduced state. The figure 2 displays the application name on the taskbar of a maximised window.
7. Close Button: It is the third button out of three buttons displayed on the right end of title bar. A click on this button will close the current window. The keyboard shortcut for this command is ALT + F4.
8. Status Bar: The status bar is displayed at the bottom of the window. It provides additional details about the window. The contents of status bar may be different for different windows.
9. Scroll Bars: Scroll bars are displayed on the right as well as bottom end of screen. The scroll bars are displayed depending upon the size of the window. These bars display the contents of the current window when the size of the window is small and the contents are more. In this case, the contents are slided by using scrollbars. The vertical scrollbar moves the contents in up and down direction and horizontal scrollbar moves the contents to right or left direction.
10. Window Borders and Corners: Every application window has a well defined size and border. The size of the window can be increased by stretching it from any of the four corners or border walls. Widows are generally resized from their corner points because the height and width of the window increases or decreases in equal proportion. This topic has been discussed in detail in the following pages.
STARTING A
PROGRAMME
This enables us to run a particular application from its
associated executable file. For example, if you type WINWORD in the run dialog
box and click OK. MS Word will be
started. This is because winword.exe is the name of executable file required to
run MS Word. You can select the desired executable file by clicking the Browse button.
You can also use Run dialog
box to directly open a particular folder of a drive. Type the path of folder
and click OK to view the contents of
the folder. For example, if you type C:\Windows and click OK, the contents of Windows folder under C drive will be displayed.
Refer to fig.
Run Dialog box
Shutdown: This option displays a dialog box that is used to turn off
the computer, restart the computer or put it on standby mode. Shutdown is very
important for any windows (95 or later version) based computer as it makes sure
that no data remains unsaved and every application has been properly closed
• Standby
option will put your computer on standby mode. This mode is used when the computer is
idle. In this mode, the monitor and
hard disks are
powered off and the computer consumes less
power. On pressing a key from the
keyboard or moving a mouse, the
computer switches back
to normal mode
Shutdown option will turn off your computer.
Restart option will restart the computer after shutting
down.
Log Off option enables you to login with another
username and password.
File
Information on a computer is stored in the form of files.
A file may include
pictures, data and
even songs. It is similar to a physical file that you use for storing
relevant information. A computer represents
files with icons. By looking at the
file's
icon, we can immediately tell what kind
of file it is.
FOLDER
A folder is like a container in which you can store
similar types of files. It helps in arranging the files into organized groups
which makes it easy for the user to locate any particular file.
 | ||
| Folders
VIEWING THE
CONTENTS OF A HARD DRIVE
Viewing the contents of a hard drive is possible using
Windows Explorer, a tool integrated into Windows operating systems since
Windows 95. The step by step
procedure to view contents of a drive is as
follows:
1. Click "Start" and select
"Computer" to open Windows Explorer .
2. Click "Tools" from the toolbar and select
"Folder Options."
3.Click the "View" tab.
4 Click "Show Hidden Files,
Folders, and Drives" from the Hidden Files and Folders list as shown below:
|









All businesses that depend on the computer repair industry rely on the Internet to do their work. If you are curious to know more about same day service, visit here.
ReplyDeleteMust read, not only this but all other blogs also informative. Get JOB placement with IT training at Webgurukul.
ReplyDeleteVisit for details: https://webgurukul.co.in
For more features and service, you can take a look at other packages. If you are curious to know more about server hosting, head over to the website.
ReplyDeleteThe free features can be anything, but they usually include a free dedicated IP address, a free FTP account, or the ability to download certain programs from their Perth servers.
ReplyDelete